Main Differences Between Muxponder and Transponder
2023-02-17
In fiber optic communications, muxponders can combine multiple services into one wavelength by utilizing ITU Optical Transport Network (OTN) protocols to map multiple services onto the same uplink. Muxponders can maximize fiber capacity by reducing the number of wavelengths needed to transmit data, making more efficient use of fiber and making them ideal for future network growth. Operators, ISPs and other industries often use multiplexing repeaters because they have operator-level functions, such as flexible remote monitoring and management, link diagnosis tools, and two-way performance monitoring of client service interface and uplink.
Transponders are often used to extend the optical transmission distance through wavelength conversion. It passes through 3R (retiming, reshaping and re-amplifying) or maps the optical signal on the client side to the optical transmission network, converts it into an electrical signal, and then converts it back to the optical signal to the line side. Implementing 3Rs ensures a reliable and error-free optical communication link.
Transponders can eliminate the need for generators by mapping the signal to a standard OTN that supports forward error correction (FEC) in long-haul and metro amplification links. Transponders are usually classified according to their data rate and signal transmission range. Operators, ISPs, and other industries often deploy transponders to build backbone and DCI networks, or provide managed services to enterprises.
The Main Difference Between Muxponder and Transponder in OTN network
In fiber optic communication, both transponders and muxponders are components that receive and transmit signals over optical fibers. Muxponder combines multiplexed low capacity services into a high capacity single wavelength. Transponder converts every optical signal from the user equipment into a wavelength.
The main difference between a muxponder and a transponder is that a muxponder has the additional ability to combine multiple services into a single wavelength by multiplexing multiple channels into a higher order signal, thus making more efficient use of fiber than transponders.
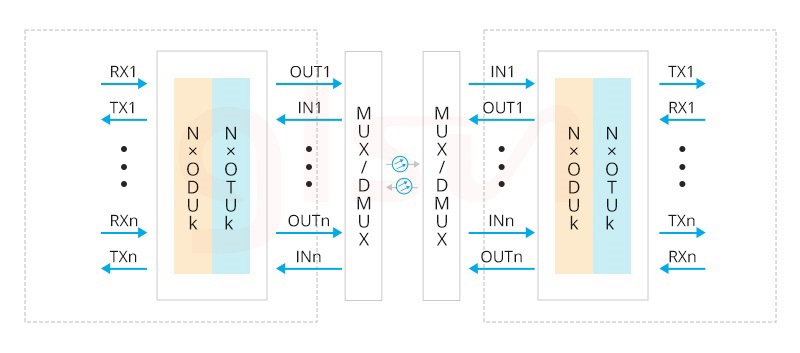
The Role of Transponders and Multiplexers in WDM Network
Transponders and muxponders are used to implement OEO (Optical-Electrical-Optical) applications in WDM networks. The functions mainly include:
· Amplifies Optical Signals – Converts a weak input signal into a strong output signal.
· Multi-mode to single-mode - To extend the transmission distance by converting multi-mode to single-mode
· Fiber Type Conversion - Maximize fiber capacity through fiber type conversion.
· Optical wavelength conversion—WDM solutions are realized through optical fiber wavelength conversion.
Transponders and muxponders can automatically receive, amplify, and retransmit signals at new wavelengths without any change to the data carried on the signals, which is not possible with transceivers alone.
The WDM solution of transponder or muxponder is a good choice. When transceiver and switch are not fully compatible or the transceiver alone is not enough to meet the needs of users, faster speed and longer transmission distance and higher security are required.
1. Encrypted network, muxsponders and transponders will help protecting sensitive data and meet encryption regulatory requirements.
2. Long-distance data transmission, transceivers do not support long-distance WDM, OEO-based transponder and muxponder solutions can extend the distance of WDM networks through FEC error correction.
3. When the ISP needs to switch a gray signal to the end user, transponders and muxponders make it possible and make it easier for ISPs to limit the bandwidth of optical connections.
4. When data needs to be transmitted in WDM network at a higher rate than transceivers, transponders and muxponders are a way to support faster rates.







