FOADM vs. ROADM
2023-06-08
Before talking about FOADM and ROADM, let's learn about what's OADM (Optical ADD/Drop Multiplexer) firstly.
What’s OADM?
First of all, OADM is a device used in WDM networks, in which the main function can be to couple two or more wavelengths into the same optical fiber to increase the total bandwidth between two points. In a traditional WDM network, the optical layer division and multiplexing part usually includes an OMU optical multiplexer, an ODU optical demultiplexer, and an OADM optical demultiplexer in the middle. OADM is divided into FOADM (short for Fix Optical Add-Drop Multiplexer) and ROADM (short for Reconfigurable Optical Add/Drop Multiplexer, is a programmable version of OADM).
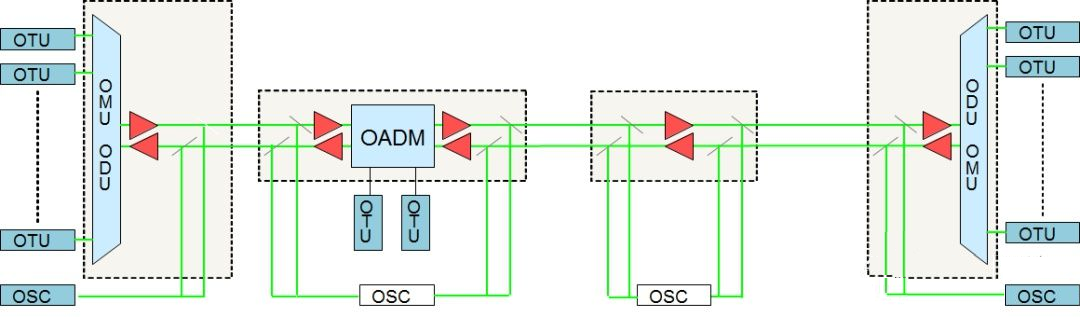
What’s FOADM?
FOADM(Fix Optical Add-Drop Multiplexer), as the name suggests, the number of wavelengths is fixed and the direction of light is fixed. The fixed optical add-drop multiplexer can only add and drop channels with specified wavelengths, and cannot dynamically adjust the settings to add and drop other channels.
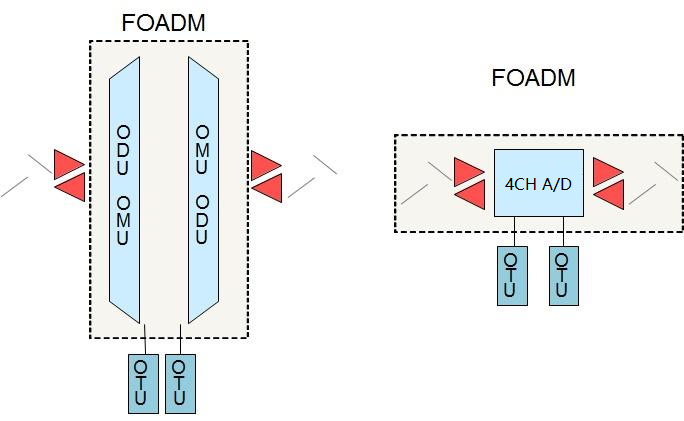
In the FOADM structure above, OADM board may include the splitting and multiplexing function, such as a 4/8 channel add/drop multiplexer board. It also can be two groups of OMU/ODU, back to back to form FOADM.
What’s ROADM?
ROADM (Reconfigurable Optical Add-Drop Multiplexer) is a device or equipment used in a Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) system. Its function is to dynamically add or drop service wavelengths through remote reconfiguration. That is to say, in the middle of the line, the wavelength of the up and down services can be assigned arbitrarily according to the needs, so as to realize the flexible scheduling of the services. In ROADM, WSS (Optical Wavelength Selective Switch) is used to add/drop arbitrary single-wave or multiplex signals from multiplexed signals, and realize multi-dimensional dynamic optical wavelength scheduling.
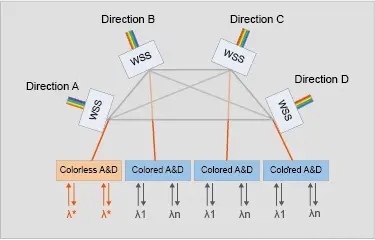
Internal Structure of WSS
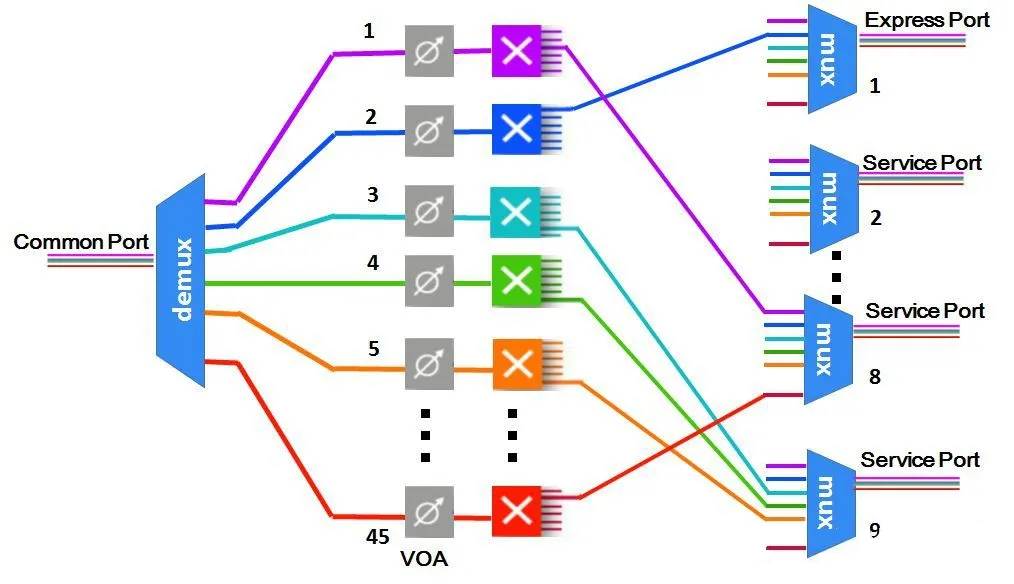
After the network node adopts ROADM, the network management system can control a certain wavelength to pass through the optical node or drop off from the local port. Fast service assignment, more automated processing, and simplified network planning and construction make it more powerful in network monitoring and network expansion capabilities than traditional wavelength division (OTM/FOADM).
At present, ROADM has evolved into multiple functions:
Wavelength: Any port can be configured with optical transceivers of any wavelength. When the wavelength needs to be changed, only software configuration is required.
Direction: Any local service can be configured to be sent in any direction, or services in any direction can be configured to be dropped locally, and only software configuration is required to change the direction.
Competition: The feature of competition-independence enables multiple services of the same wavelength to be added and dropped on the same local node, which simplifies network design and improves port utilization.
Flexible Grid (flex-grid): New modulation formats and signal baud rates require that the channel spacing can be adjusted more flexibly to achieve better spectral efficiency. Through the software, the channel center wavelength and interval can be arbitrarily configured in steps of integer multiples of 6.25 GHz.
The combination of the above functions can realize a variety of ROADM architectures.







