What are the Key Components of an Optical Isolator?
2024-07-05
Optical isolators are essential components in fiber optic communication systems, laser applications, and various other optical setups. They are designed to allow light to pass through in one direction while blocking any light that attempts to travel in the opposite direction, thereby providing optical isolation. This one-way traffic control helps prevent damage to sensitive equipment, reduce noise, and enhance system performance. Understanding the key components of an optical isolator can help appreciate its functionality and importance in various applications.
An optical isolator typically comprises three primary components:
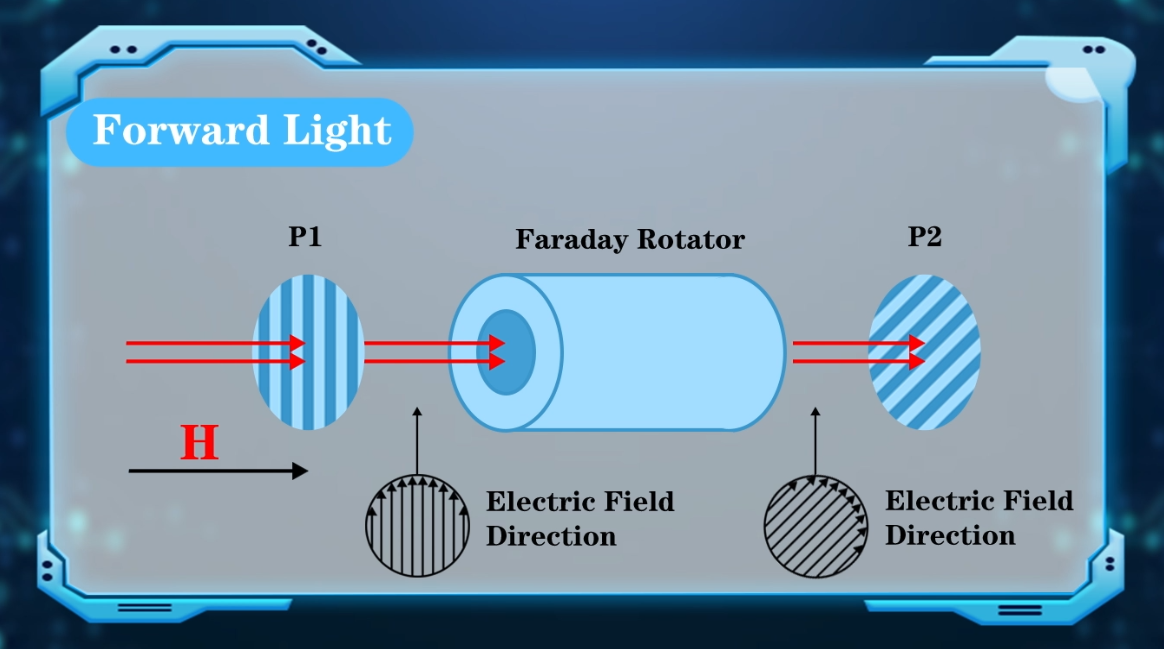
1. Input Polarizer: This component acts as a gatekeeper, allowing only light with a specific polarization orientation to pass through. It effectively filters out any unwanted, randomly polarized light.
2. Faraday Rotator: As discussed earlier, this component forms the core of the isolator. It utilizes the Faraday effect to rotate the polarization plane of the incoming light by 45°.
3. Output Polarizer: Positioned after the Faraday rotator, the output polarizer is aligned to transmit light with a 45° polarization relative to the input polarizer.
Now, let's see these components in action:
Forward Propagation: Light entering the isolator first encounters the input polarizer. Only light polarized in the designated direction passes through. This polarized light then enters the Faraday rotator, where the magnetic field causes a 45° rotation. The now rotated light aligns perfectly with the output polarizer's transmission axis, allowing it to pass through unimpeded.
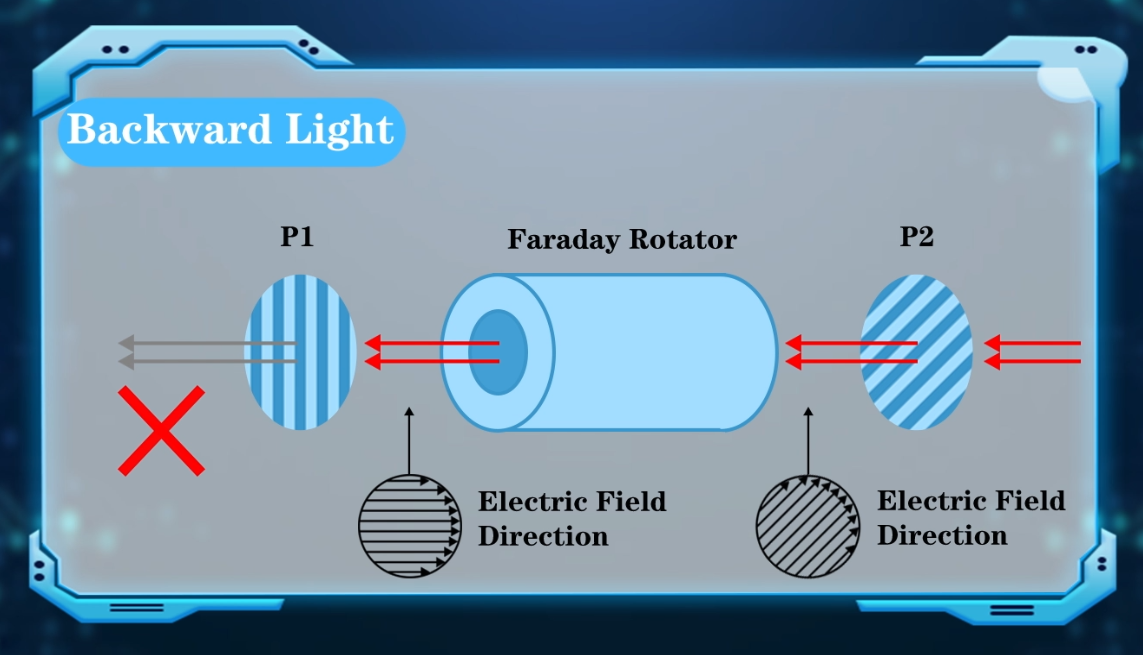
Backward Propagation: Any light attempting to travel back through the isolator faces a different fate. The output polarizer first filters it, allowing only light with a 45° polarization to pass. However, upon entering the Faraday rotator, the magnetic field rotates this light by another 45°. This rotation results in a 90° polarization shift compared to the input polarizer, effectively blocking it from exiting the isolator.
Optical isolators are indispensable in numerous applications, including:
1). Protecting Laser Sources: Isolators prevent reflected light from entering the laser cavity, which can cause instability and damage.
2). Enhancing Signal Quality: In fiber optic systems, they prevent back-reflections, ensuring clear and stable signal transmission.
3). Improving Measurement Accuracy: They are crucial in optical instruments, preventing spurious signals from affecting measurements.
At GLSUN, we understand the critical role optical isolators play in various technologies. That's why we offer a comprehensive range of high-quality optical isolators designed to meet diverse needs. Our products are crafted with precision and utilize superior materials to deliver exceptional performance, reliability, and durability.
Whether you require isolators for high power lasers, telecommunication systems, or any other application, GLSUN has the perfect solution for you. Browse through our selection of optical isolators.







