What Are the Different Polarity Types for MTP/MPO Cables?
2024-09-30
MTP/MPO cables are widely used in high-density fiber optic networks, particularly in data centers, due to their ability to support multiple fibers in a single connector. A crucial aspect of ensuring efficient performance in these networks is understanding the different polarity types of MTP/MPO cables. Proper polarity ensures that the signal is transmitted correctly between transmitters (Tx) and receivers (Rx).
Polarity refers to the alignment of fibers within an MTP/MPO cable to ensure that the transmitted signal from one end of the cable reaches the correct receiving end at the other. MTP/MPO connectors can house multiple fibers (usually 8, 12, or 24), which adds complexity to maintaining correct signal transmission. Without proper polarity management, signals can end up mismatched, leading to connection failures and decreased network efficiency.
There are three main polarity types for MTP/MPO cables: Type A, Type B, and Type C. Each type has its own characteristics and applications in different network configurations.
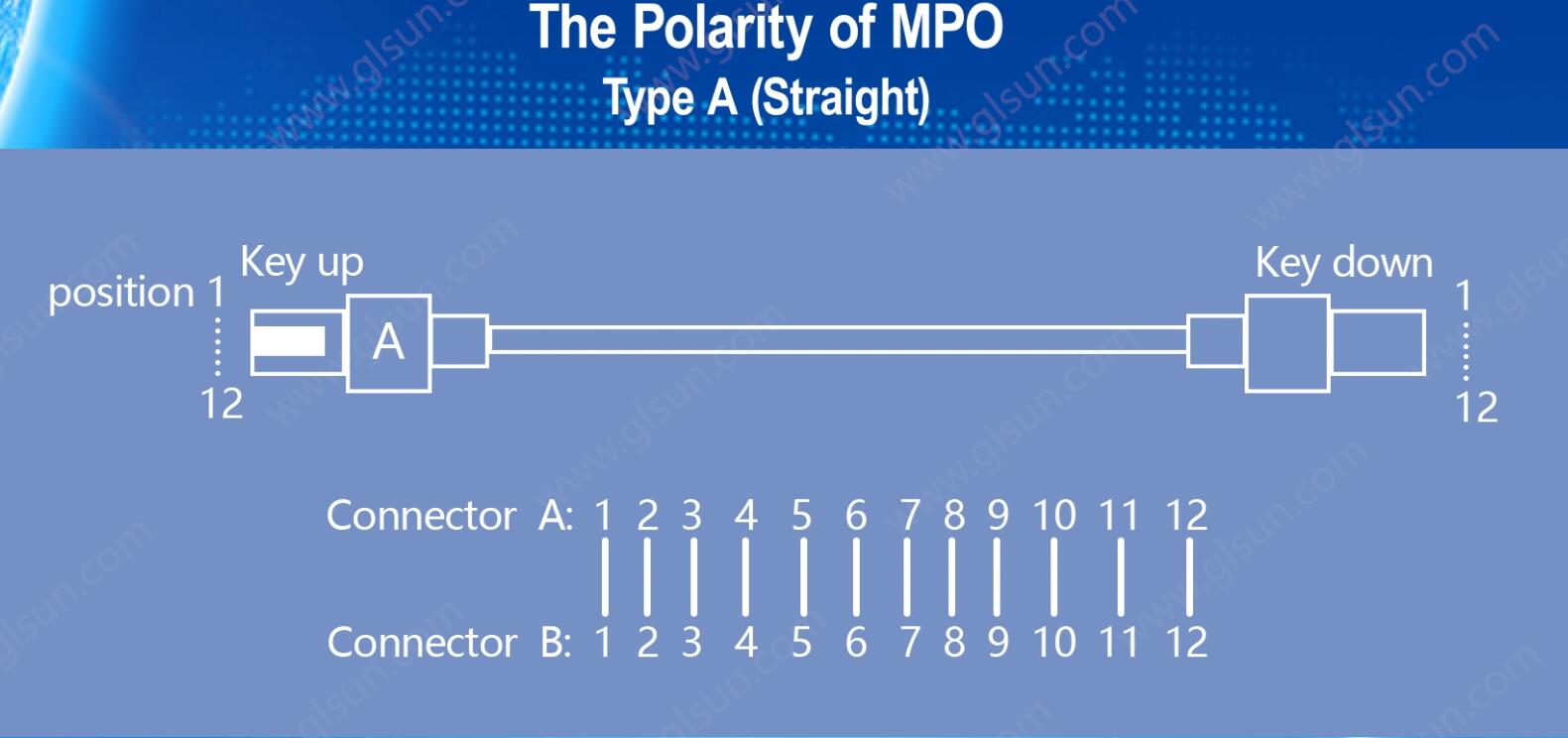
1. Polarity Type A (Straight)
In a Type A cable, the fibers are aligned in a straight-through configuration. This means that the fiber at position 1 on one end of the cable is connected to position 1 on the other end, and so on for the rest of the fibers. The fiber order remains the same from one connector to the other.
Key Applications:
Type A cables are typically used in situations where patch panels are deployed at both ends, as the cross-over can be managed at the patch panel.
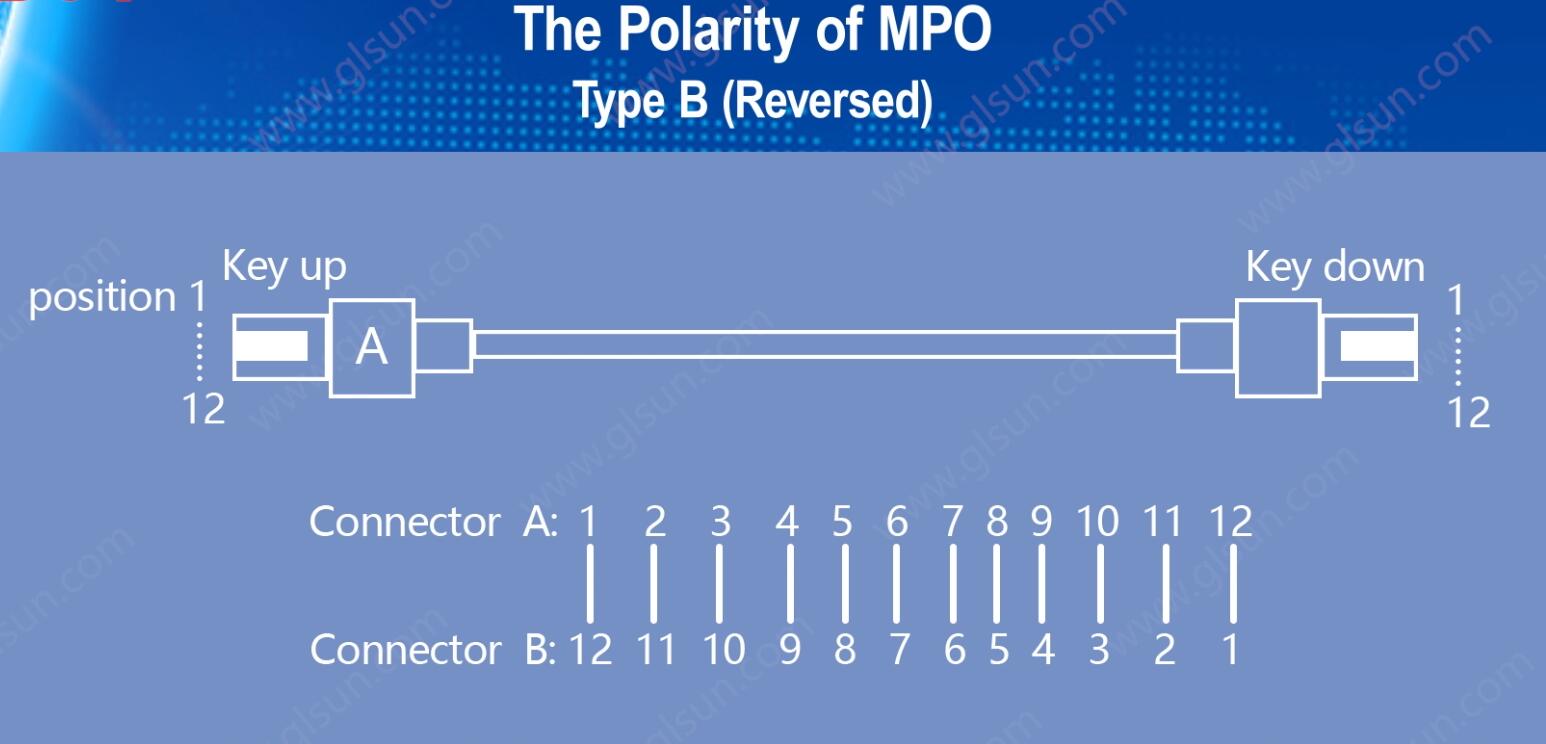
2. Polarity Type B (Reversed)
Type B cables have a "reversed" fiber configuration. In this type, the fiber at position 1 on one end is connected to position 12 on the other end, and so on, with position 2 connected to position 11, and so forth. This creates a flip or reverse in fiber alignment.
Key Applications:
Type B cables are commonly used in transceiver-to-transceiver connections, as the flip ensures that the transmitter and receiver are correctly aligned without additional intervention.
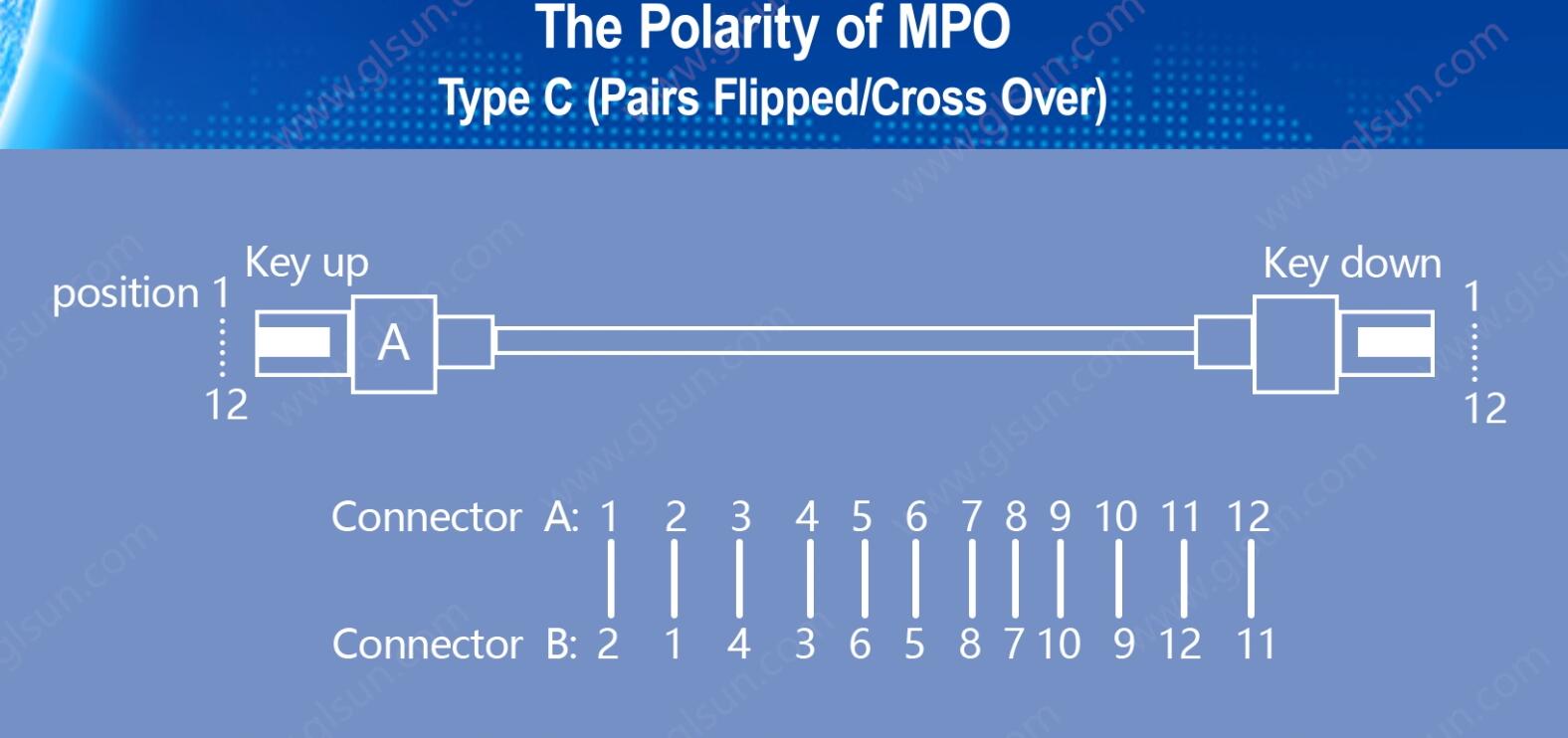
3. Polarity Type C (Pairs Flipped)
In a Type C cable, adjacent fiber pairs are crossed. For example, fibers 1 and 2 are swapped with fibers 2 and 1 at the other end, and this pattern continues across all pairs in the cable. This configuration is used to accommodate different fiber arrangements and is designed to make polarity management easier when multiple cables are used in trunk configurations.
Key Applications:
Type C is primarily used for structured cabling systems, particularly in environments that require rapid changes and easy polarity adjustments.
To maintain proper polarity in MTP/MPO cables, it is essential to:
1. Identify the type of polarity used in the network setup.
2. Ensure that patch panels, adapters, and connectors are correctly configured to match the polarity requirements.
3. Use pre-terminated cables with standardized polarity methods to simplify network installation and avoid potential errors.
Understanding the different polarity types for MTP/MPO cables—Type A, Type B, and Type C—is essential for maintaining efficient and reliable fiber optic connectivity in modern data centers and high-density networks. Selecting the appropriate polarity method can help avoid connection errors and ensure optimal network performance.
GLSUN offers a range of MTP/MPO fiber optic solutions tailored to meet the needs of high-density and high-bandwidth environments.







